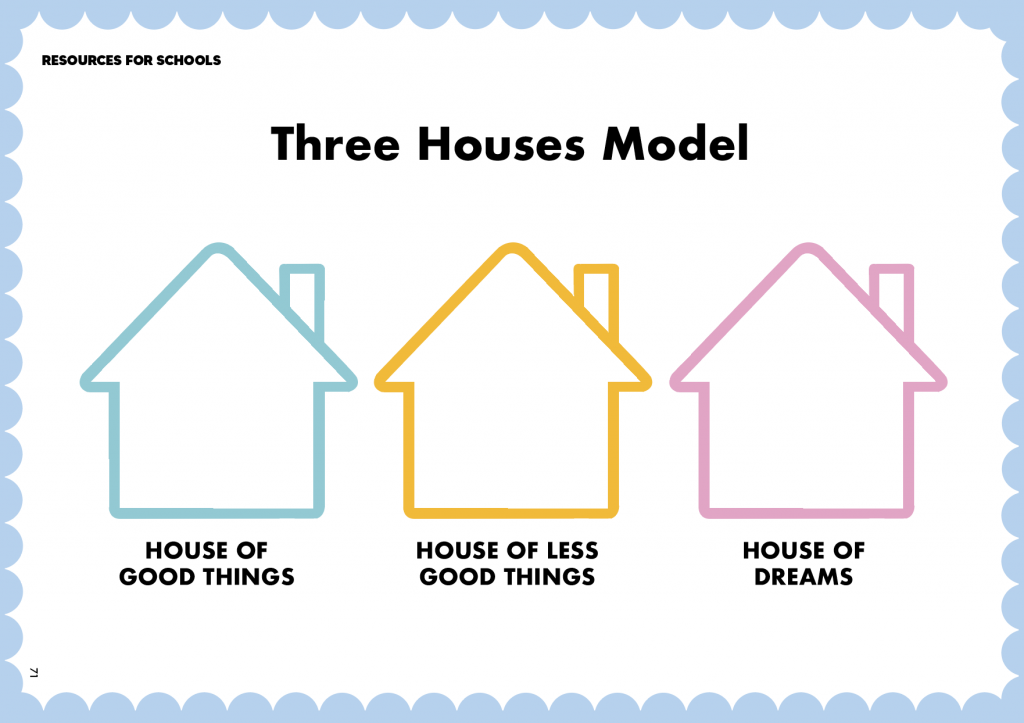
How can a Life Skills Curriculum Support Children to Access Learning?
Danielle Petar

‘More than just practising daily tasks…’ Gesher’s new life skills scheme
The idea of teaching life skills in schools as part of a young person’s education has been formalised since the late 1990s when the World Health Organisation (WHO) introduced its ten core life skills principles. They defined life skills as ‘a group of psychosocial competencies and interpersonal skills that help people make informed decisions, solve problems, think critically and creatively, communicate effectively, build healthy relationships, empathise with others, and cope with and manage their lives in a healthy and productive manner’. Before that, it was a core mission of the scouting movement (since the 1920s) and the Duke of Edinburgh’s Award (founded in 1956). We have long known that life skills are an essential thing to have. For specialist schools like Gesher, they are crucial to school success, future life chances and emotional well-being.
Despite this, what the student experience of life skills learning means for day-to-day teaching can be difficult to picture. Is it discrete individual lessons about part of the WHO’s definition? Is it traditional lessons like maths, literacy, and science which implicitly teach these skills? Is it practising skills that young people will need for daily life in their classrooms and beyond? Is it something which teachers teach, or should this learning be happening at home?
What the student experience of life skills learning really means for day-to-day teaching can be difficult to picture.
These are some of the problems that Gesher’s Inclusion Team, (Danielle Petar and Matt Summers), grappled with when they first set out to develop Gesher’s own life skills scheme at the start of 2020 — and they are sharing their experience in the hope that it will be of value to others. Two years on, this scheme, called Bridges: Foundation, has been launched to Gesher’s students and will shortly also be introduced to parents. In anticipation of this, we sat down with Danielle and Matt to find out more about the journey they went on to design the scheme as well as some of its features.
Setting Up The Scheme
‘The notion of creating something which meets all of the WHO definition of life skills was exciting but also rather daunting. In the first stage of the process, we looked at the four key areas in the Government’s ‘pathway to adulthood’ guide. These are employment; independent living; good health; and friendships, relationships and community. However, we quickly realised that we’d need some more focus and to break these down further’. After going through various combinations of themes, the team decided on eight child-friendly themes.
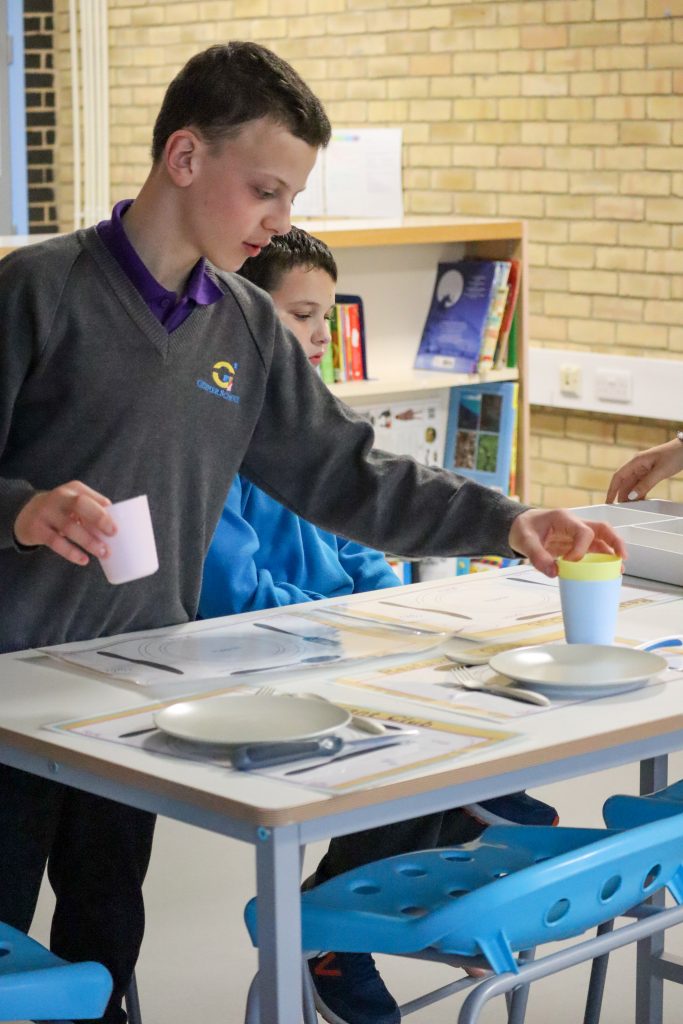
 Within each of these themes, there are eleven badges for the students to work towards achieving. In the ‘My Home’ theme, for example, the badges range from ‘Clearing the Table’ to ‘Preparing for Social Occasions’. ‘While each badge is very different they are all designed to focus on developing creativity, critical thinking, problem-solving, decision-making, the ability to communicate and collaborate, as well as commitment to personal and social responsibility.’
Within each of these themes, there are eleven badges for the students to work towards achieving. In the ‘My Home’ theme, for example, the badges range from ‘Clearing the Table’ to ‘Preparing for Social Occasions’. ‘While each badge is very different they are all designed to focus on developing creativity, critical thinking, problem-solving, decision-making, the ability to communicate and collaborate, as well as commitment to personal and social responsibility.’
The approach is driven by the student’s motivation to learn new skills, explore their areas of interest and develop their independence, as well as encouraging them to think about their future. Therefore, they have some autonomy in choosing their badges.
‘We were also eager to ensure that the young people themselves were included in the design process and it’s safe to say their feedback was refreshingly honest… It ultimately had a huge impact on the way the scheme looks from a visual perspective. Given that it’s the young people themselves who will be using the scheme, this is exactly what we wanted.’
The final stakeholder group that Danielle and Matt sought views from while in that crucial design phase was parents from the Gesher community. ‘The scheme was designed as an exciting journey that would foster a partnership between home and school, with students completing badges both at home and at school. As parents were going to be a vital part in implementing it, then it was equally important to get their input in the design process.’

Taking Ownership
The design of the Bridges scheme was very much focused on ensuring that students can take ownership of their learning. Within each life skill, there are four ‘steps’ to achieve along their journey that reflect an increasing level of independence and in this way students can see their progress.
As you journey through the different life skills badges, there are different steps along the way that you can take; each step leading you to be more independent.
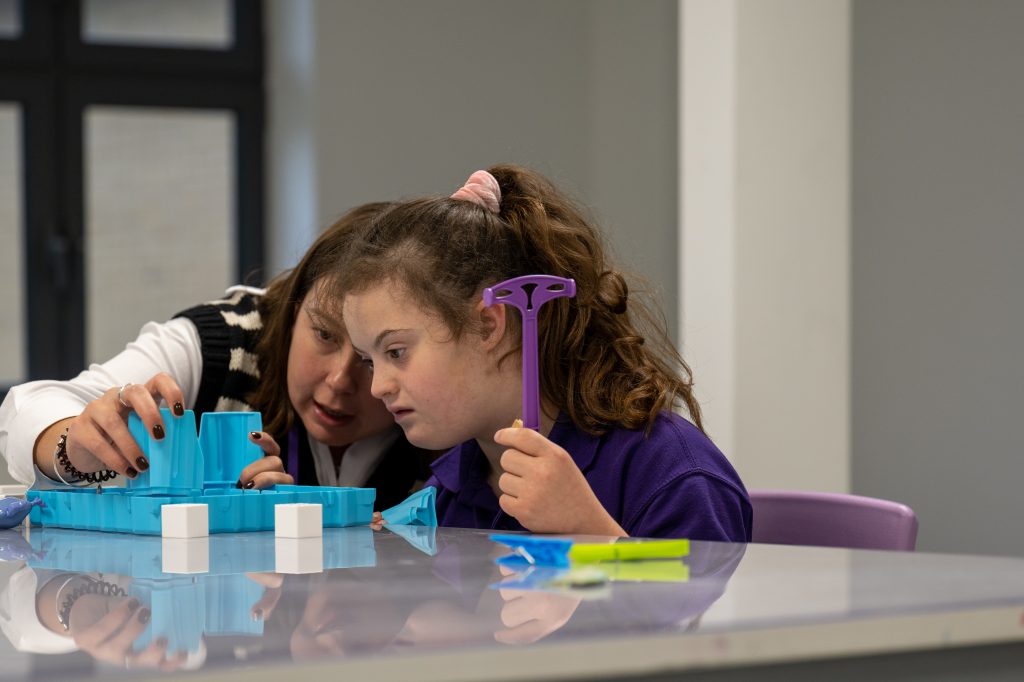
Each step has a number of success criteria provided, which are visible and accessible to students. These were created by extensive research from the Inclusion team and in consultation with a wealth of other educational professionals (Occupational Therapists, Speech and Language Therapists, Educational Psychologists, Art Therapists, Teachers, Teaching Assistants and Dramatherapists).
The different steps are not age-related but rather based on a child’s own stage of development at any given time. Both the approach and the journey navigation are highly personalised.
‘Unlike the way that learning is normally structured, both the approach and the journey navigation are highly personalised. The different steps are not age-related but rather based on a child’s own stage of development at any given time and based on their individual skills and needs. We did this to reflect the fact that a young person’s journey to adulthood is not linear and they will navigate their own winding path.’ Put another way, both the approach and the journey navigation are highly personalised.
Beyond Practising Daily Skills and Student Ownership
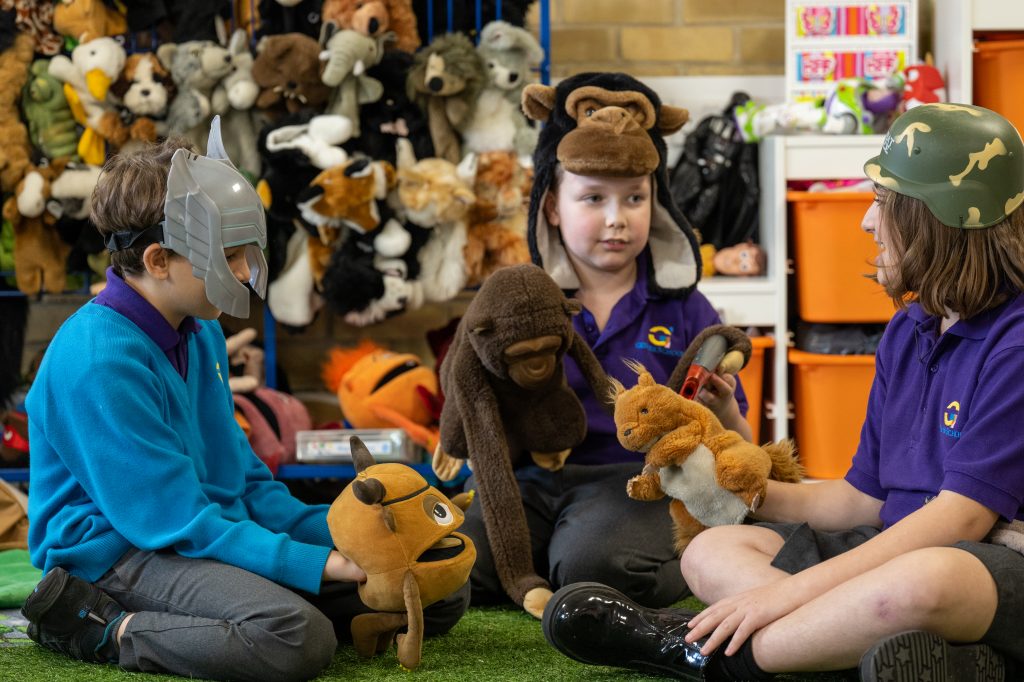
Unlike more traditional life skills schemes, Gesher’s reach is broader in terms of the themes it covers and has a greater focus on softer skills like decision-making and critical thinking. ‘We wanted the scheme to be aspirational, more than a means by which to practise daily tasks.’ This is evident in the inclusion of themes like ‘My Imagination’ and ‘My World’, which encompass skills like ‘Making a gift’ and ‘Learning about a religion’.
This breadth means that young people don’t just work on their life skills badges in the classroom but in a home context as well. ‘The success criteria for each level have been designed to include language that is accessible for students as well as the adults in their lives.’ To further promote this, students work on a minimum of three badges at a time. The idea is that one is chosen by their teacher to work on in the classroom and relates to their project-based learning; one is chosen alongside the adults at home; while the last is selected by the young people themselves. This badge they will work on both at home and at school. ‘Obtaining these badges at home and at school should be both meaningful and fun and will hopefully open up new experiences for students as they navigate their own journeys to adulthood. It’s also important to say that there is no limit on how many badges a student can be working on at any one time. The scheme is designed to give them the opportunity to explore and to be ambitious.’
Hiding in Plain Sight
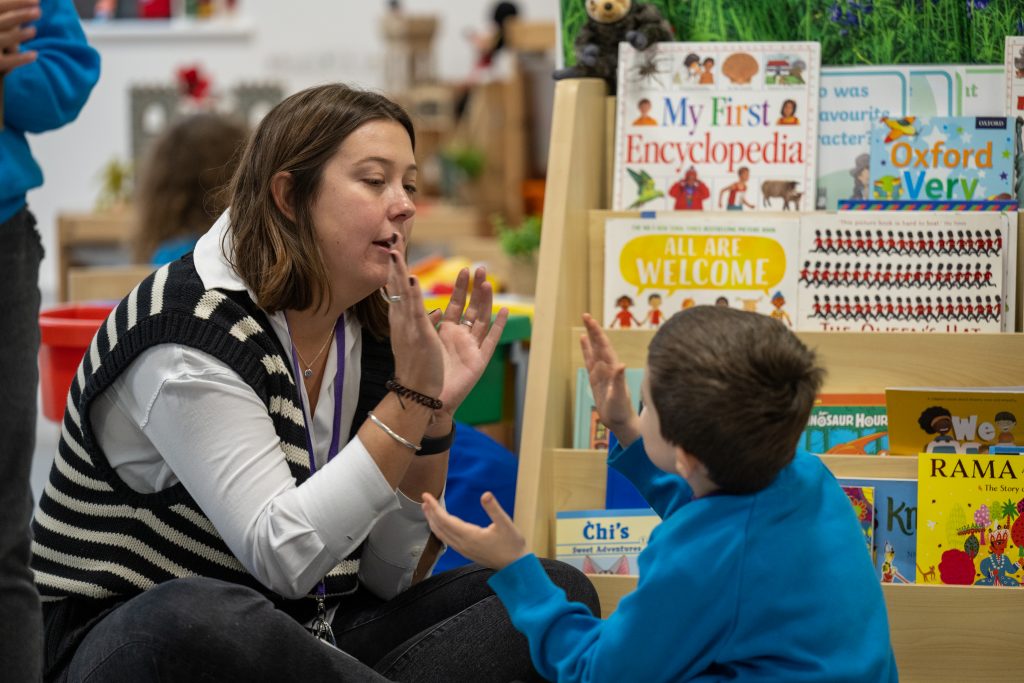
The eight themes ensure that the life skills curriculum is incorporated across the school from the Early Years class to the students in Year 8. This will allow students to become familiar with the skills they need for adulthood as early as possible in their education journey. Each class has one discrete life skills session a week where they work on their chosen badges. This is led by the school’s ‘life skills champion’ and the class teacher. In addition, for students at Gesher who are less likely to graduate with traditional academic qualifications such as GCSE and may follow a more vocational route, life skills sessions are taught daily in small groups.
As well as this dedicated time, the school’s holistic approach to learning means that badges can be worked on during students’ therapy sessions or in-class sessions through project-based learning. What will be obvious is that the approach (student ownership, personalisation, real-world tasks, school and community, etc) has many features in common with the project-based learning approach to the wider curriculum.

Next Steps
Whilst the Bridges scheme is very much underway, it will evolve and the team is already planning to create further resources to support the teaching of each life skill. They are also in the process of creating the next stage of the scheme, Bridges: For Life. This will expand on the four areas of preparing for adulthood and ensure that the students build on the life skills they’ve already developed through the Foundations scheme. This article offers a window into an important aspect of our work, one of which we are proud — both the scheme itself and the process through which it was developed. If you want to know more, please contact Gesher.
Legacy
Gesher is both privileged and humbled that this scheme has been made possible by working in collaboration with the Daniels family in order to honour the extraordinary life of Sonya Daniels, their wife, mother and grandmother.
Professional Prompt Questions
-
We all know how important life skills are for young people. How well established is (a) your curriculum for life skills; (b) your assessment processes?
-
In particular, how coherent is your life skills work with SEND youngsters?
-
Does the idea of badges have any merit for you?



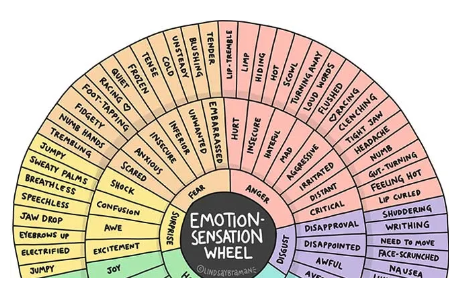


 Within each of these themes, there are eleven badges for the students to work towards achieving. In the ‘My Home’ theme, for example, the badges range from ‘Clearing the Table’ to ‘Preparing for Social Occasions’. ‘While each badge is very different they are all designed to focus on developing creativity, critical thinking, problem-solving, decision-making, the ability to communicate and collaborate, as well as commitment to personal and social responsibility.’
Within each of these themes, there are eleven badges for the students to work towards achieving. In the ‘My Home’ theme, for example, the badges range from ‘Clearing the Table’ to ‘Preparing for Social Occasions’. ‘While each badge is very different they are all designed to focus on developing creativity, critical thinking, problem-solving, decision-making, the ability to communicate and collaborate, as well as commitment to personal and social responsibility.’




 Some Lessons For Any School
Some Lessons For Any School